
Internet of things commonly abbreviated as IOT is a network of internet-connected objects able to collect and exchange data. Any device or object that can collect and exchange data over a network are referred to as “connected devices” or “smart devices” and are part of internet of things. The IOT may be a hot topic in the industry but it’s not a new concept. It has been in development for decades. The first internet appliance, for example, was a Coke machine at Carnegie Melon University in the early 1980s which could report its inventory and also could tell whether newly loaded drinks were cold. Today IOT is everywhere around us, smart cars which drives themselves are IOT, smart phones and computers bringing doctors and patients together virtually are IOT, smart buildings that reduces energy costs are IOT, its a world of things.. making a world of difference. According to Gartner, Inc. (a technology research and advisory corporation), there will be nearly 20.8 billion devices on the Internet of things by 2020. ABI Research estimates that more than 30 billion devices will be wirelessly connected to the Internet of things by 2020. Here are 5 IOTs which have made our life simpler.

Figure 1.1 Basic of IoT
Wearable’s (Smart Watch/ Heart Monitor/ Headphones/ VR)
2.1 Problem and Solution
- Problem:
- For most of the people, it is not possible to carry smartphones during activities like jogging, swimming etc. we can not use smartphones as our fitness monitor because we cannot wear it, so people wanted a device which can be continued in contact with the human body and provide complete monitoring of health-related issues.
- Solution:
- As the name suggests, Wearable devices are quite handy and easy to use, we can wear them while jogging and swimming, we don’t need to carry our smartphones everywhere. Plus some of these devices can be used as a fitness tracker and they can be connected to our smartphones.
2.2 Basics of Wearable’s
In a 2002 report titled Converging Technologies for Improving Human Performance, the U.S. National Science Foundation predicted that, within the next two decades, “Comfortable, wearable sensors and computers will enhance every person’s awareness of his or her health condition, environment, chemical pollutants, potential hazards, and information of interest about local businesses, natural resources, and the like.” Twelve years later, the future that the National Science Foundation predicted is starting to emerge.
The main objective of the development of Wearables is to get mobility in a different way. These small devices are more lightweight and user-friendly yet more efficient in performing various functionalities related to capturing input and monitoring activities. Wearable devices are installed with sensors and software which collect data and information about the users. This data is later pre-processed to extract essential insights about user.
These devices broadly cover fitness, health and entertainment requirements. The prerequisite from internet of things technology for wearable applications is to be highly energy-efficient or ultra-low power and small sized.
Here are some top examples of wearable IoT devices that fulfill these requirements.
-
Cicret Bracelet
The concept of this product uses a band that puts your device’s home screen on your wrist. This wristband brings full smartphone functionality to your arm. It’s all built around a tiny projector stashed inside the wristband. Aside from replicating your phone’s screen, it is also able to detect movements and inputs. The proximity sensor can track what is happening and relays commands to your device via Bluetooth. Cicret band is able to mirror Android, Apple and Windows Phone devices.

figure 2.1 Cicret Bracelet
-
LECHAL GPS Shoes
Navigational maps on the phone might be a big support for the die-heart trekker. But it is a pain having to walk unknown territory with your eyes glued to your smartphone’s screen. With these pair of Bluetooth-connected shoes that use haptic feedback to notify users which direction to take, navigational maps might become 5assé. You can buy ‘LECHAL’, (‘take me along’ in Hindi) as either a set of shoes or a set of insoles. Using GPS the app determines directions and notifies the user which side to turn by sending a mild vibration to the right or the left shoe. The app also functions as a fitness tracker and lets you check your record at places.

figure 2.2 LECHAL GPS Shoes
-
Smartwatch
Smart watches are digital watches that are much more than the conventional analog or digital watches. These watches are full fledged digital tools. Smart watches can run apps and play all sorts of digital media, like audio tracks or radio streamed to Bluetooth headphones. Many of these watches have touchscreens, which allow you to access functions like a calculator, thermometer, compass and more. Some smart watches are made specifically for athletics purposes, letting you track your lap times, distance and route. They may work in sync with accessories such as a heart rate monitor or cadence sensor.

figure 2.3 Smartwatch
-
More Wearable devices
- NuMetrex Fabric Chest Strap
- Google glass
- VR Virtual reality
- Smart water bottle
Smart Home (Apple Home Kits)
3.1 Problems and Solution
- Problem:
- Forgot to switch off the lights at home which leads to large electricity bills.
- Always risk of theft in house.
- Users spends a lot of money for owning a house.
- Solution:
- Automate lights and control them from anywhere so can save money on energy bills.
- Easily secure your home.
- The cost of owning a house is the biggest expense in a homeowner’s life. Smart Home products are promised to save time, energy and money.
3.2 Basics of Smart Home
Smart Home technology intelligently gives you ultimate control over your home by automating the lighting system, dimming, blinds, electrical appliances, audio and security systems. Smart homes connect all the devices and appliances in your home so they can communicate with each other and with you.
3.2.1 What’s Smart Home?
A smart home is one in which the various electric and electronic appliances are wired up to a central computer control system so they can either be switched on and off at certain times (for example, heating can be set to come on automatically at 6:00 AM on winter mornings) or if certain events happen (lights can be set to come on only when a photoelectric sensor detects that it’s dark).
Smart homes may look like ordinary houses, however they are anything but passive and neutral. They intelligently and autonomously observe inhabitants’ activities, learn their behaviors and routines to predict and act accordingly, and adapt to changes of environment or people. These tasks are all possible as consequences of smart homes’ two main characteristics which are context-awareness and strong connectivity.
So, for example, it monitors light levels coming through the windows and automatically raises and lowers blinds or switches the lights on at dusk. Or it detects movements across the floor and responds appropriately. if it knows you’re home, it switches light and music on in different rooms as you walk between them; if it knows you’re out, it sounds an intruder alarm.
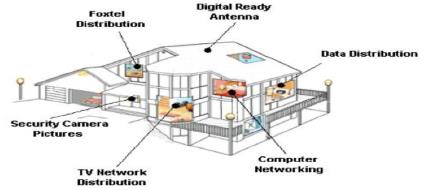
figure 3.1 Smart Home Basic
- Features of Smart Home
- Home Security System
- Controlled Exterior & Interior Lighting
- Automatic Window and Curtain
- Automatic Garage Door
- Distributed Entertainment Systems (Video and Audio systems)
- Intercom/Telephony Systems
- Home Energy management systems
3.2.2 Why Smart Home?
Smart Home is applicable in various aspect of our home and environment to suite our different preferences.
- Comfort or Ease of control:Smart Home offers ease of controlling devices around the home. This is one of its outstanding features. These features offer automation and remote control of devices around the home from any location within such as:
- Automatic control of garage door and gate(s)
- Automatic shut down of appliance when not in use
- Automatic setting and maintenance of right temperature for each room;
- Automatically adjust/ regulate light intensity based on room luminosity.
- Entertainment:Smart Home offers multi room entertainment network which enables listening of audio music and watching of movies from any part in the house.
- Easy Control: Parental control feature on television channels for children to watch only certain programmes.
- Digital Access: Access favourite CD’s, DVD’s from any music system and television around the home.
- Digital Storage: System automatically stores most played music based on number of play.
- Security:
- Security Camera
- Controlled motion sensitive cameras which allow for observation of activities.
- Capture and record video surveillance.
- Emergency
- Security Camera
- Initiate emergency alarm or audible intruder alert.
- Activate sprinkler and fire extinguishing system in case fire emergency.
- Automatic de-activation of electric systems and activate emergency light Controlled Access
- Security Camera
- Security Camera
- Health:SMART homes offers benefits for the disabled and elderly persons in the various ways:
- Monitory systems.
- Automated alarm systems directly connected to hospitals in cases of incidents like a fall or collapse.
- Alert systems for the notification on prescribed medications.
3.2.3 Apple HomeKit
Apple introduced a new system last autumn – called HomeKit – that will enable you to have wireless and electronic control of your home, household features, activities, appliances, and more.
Apple developed the HomeKit framework so it could simplify the current state of home automation. For that purpose, Apple created a common language that smart devices from any manufacturer can understand and support. HomeKit also leverages Siri, Apple’s voice assistance, so you’ll be able to control smart devices with just your voice.
The idea is that HomeKit will provide you with the ability to remotely control your home and all the smart devices inside it, You’ll no longer have to use several individual apps to control all the smart devices in your home.
HomeKit compatible brands and products
- Elgato
- iHome
- Lutron
- Insteon
- Ecobee

figure 3.2 Smart Home Devices
HomeKit allows seamless integration between iOS devices and home automation accessories, by promoting a common protocol and providing a public API for configuring and communicating with accessories. HomeKit enables a single app to coordinate and control a range of accessories from multiple vendors. Multiple accessories can act as a single coherent whole, without requiring vendors to coordinate directly with each other.
Working with Home Accessories
HomeKit allows third-party apps to perform three major functions:
- Discover accessories and add them to a persistent, cross-device home configuration database.
- Display, edit, and act upon the data in the home configuration database.
- Communicate with configured accessories and services to get them to perform actions, such as turning on the lights in the living room.
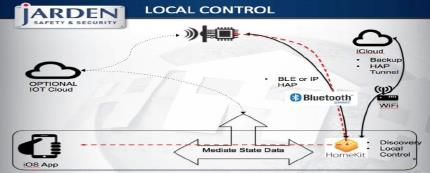
figure 3.3 Local Control for Smart Home Devices
The home configuration database is not only available to third-party apps, it’s also available to Siri. This allows users to give commands like “Siri, turn on the lights in the living room.” If a user creates a home configuration with logical groupings of accessories, services, and commands.

figure 3.4 Remote Control for Smart Home Devices
Current “Energy-as-a-service”
4.1 Problems and Solution:
- Problems:
- Traffic Accidents
- Weather warnings
- Crime
- Solution:
- This technology will help to reduced traffic accidents, Lighting controllers that use connected vehicles as sources of data. This source of data will help to reduce non-alcohol-related traffic accidents by as much as 80 percent.Sensor-enabled lamps connected to the Industrial Internet with the ability to monitor traffic, get severe weather warnings and even spot empty parking places. Crime could be next on the list.
4.2 Basics of Current “Energy-as-a-service”
In October 2015, GE launched “Current”. What is basically Current in term of technology, It’s a startup that combines energy hardware with a digital backbone to make power simpler and more efficient for customers.
Former IBM Watson executive John Gordon just became Current’s first chief digital officer. A brief introduction about IBM Watson is “IBM Watson is working with businesses, scientists, researchers, and governments. With Watson, we can analyze and interpret all of our data, including unstructured text, images, audio and video”.
At IBM, John Gordon was responsible for launching innovation programs like Smarter Cities. Intelligent street lamps developed by Current are already gathering data in San Diego and Jacksonville. They could make everything from parking to traffic and law enforcement easier. So now we have so much queries in our mind regarding this technology. What is Current?
- What’s the idea behind Current?Let’s look at intelligent lighting. What could be intelligent lighting? It’s the equivalent of the cell phone in the industrial world. Once the cell phone added data connectivity, GPS, a camera and a microphone it became a platform for innovation. It put all those sensors on a single platform and enabled developers to drive all kinds of innovation for consumers that many of us would never have thought of. lighting is already everywhere, it could be great source for innovation in the commercial, industrial, and city markets. Our intelligent LED street lamps can already see and hear things and measure air quality.
- How will it happen?They developed the core LED lighting technology with sensors. Then we can add analytics and the initial set of software solutions that will inspire the industry. The goal is to open up this intelligent lighting environment as a platform for innovation in the industrial world. Now we have a question in our mind is that.
- What kinds of applications? Outdoor intelligent lighting can help improve traffic and optimize parking. Indoors, we can use it to manage inventory and security, monitor machines and equipment, and spot problems before they break out. The applications are different but they fundamentally use the same intelligent platform. Now we have some queries regarding what operating system or software systems will help to develop this kind of application.
- Most smartphones run on iOS and Android operating systems. This makes it easy for developers to write apps. Is any other technology similar to the industrial world? Absolutely. GE developed Predix, which is a cloud-based software platform for the Industrial Internet. GE engineers are already using it to write apps for everything from wind turbines to computed tomography scanners. In September 2015, GE opened Predix to customers and outside developers so they can write their own apps. The apps will be available in an “industrial app store.”At Current, They focus on expanding and enriching the data that is available to developers and making it available to Predix. While the Predix team will build the common industrial platform, They will be adding the specific sensors – starting with LEDs data enrichments and analytics to create the “nervous system” of business.

figure 4.1 LED with Sensors
- So what is predix? Basically Predix is General Electric’s software platform for the collection of data from industrial machines. General Electric plans to support the growing industrial internet of things with cloud servers and an app store. It provides many services for IoT systems. We can say Predix is an Industrial internet.
- How closely they work with GE Digital and the team at GE’s software center in San Ramon? They starting with LED transformation and will have a significant group embedded in San Ramon and building business solutions on top of the Predix platform.
- Current would be “energy as a service.” How we can explain that? The lighting and energy system has been around for a long time and is great at transmitting electrons. But at Current we believe it can be more. Lighting and energy literally touch every corner of business and we think it can become the nervous system for organizations.
So atlast we can say about Current technology, Current will give us eyes and ears everywhere that are able to help us understand what’s going on outside. You end up with safer and more efficient cities for driving and parking, you end up with more satisfied citizens… all while paying less for energy than ever before.
Driverless Vehicle
5.1 Problems and Solution

5.2 Basics of driverless
An autonomous car (driverless car, self-driving car, robotic car) is a vehicle that is capable of sensing its environment and navigating without human input. Autonomous cars can detect surroundings using a variety of techniques such as radar, lidar, GPS, odometry, and computer vision. Advanced control systems interpret sensory information to identify appropriate navigation paths, as well as obstacles and relevant signage. Autonomous cars have control systems that are capable of analyzing sensory data to distinguish between different cars on the road, which is very useful in planning a path to the desired destination.

figure 5.1 Driverless drive
When it comes to the emerging technology of self-driving cars, major auto makers like General Motors and tech giants including Google get almost all the hype. Much of the attention is focused on how self-driving technology could affect consumers, as well as some key pockets of the market that rely on drivers, like cabs and ride-hailing apps like Uber.
- But pizza delivery is another frontier in the space, as Domino’s recent initiatives attest. The company reportedly debuted its first commercial autonomous delivery vehicle that is a four-wheeled driverless car with pizza box-sized compartments. According to ZDNet, the vehicle has already hit the streets, steered by Google maps data under tests performed under a permit in Brisbane, Australia.

figure 5.2 Autonomous Pizza Delivery Vehicle
- Google has been working on its driverless car project since 2009. Having driven more than 1.7 million miles in autonomous mode, Google’s driverless cars are arguably some of the most advanced compared to the many others in the driverless car race. Google first started testing its driverless technology using a Toyota Prius retrofitted with the tech in 2009, the year the Google self-driving car project was born. After completing 300,000 miles of testing, Google retrofitted Lexus SUVs to test its driverless tech in 2012. These cars have been tested on freeways and city streets. Google built its first driverless car prototype dubbed the ‘Koala car’ in 2014. It has no steering wheel or pedals since it’s fully autonomous.

figure 5.3 Autonomous Google Driverless Vehicle
- Driverless Vehicles and Their Future in India: As driverless vehicles become a reality, there is a need to understand what such technology could mean for urban transportation in India. Even as the penetration of autonomous vehicle technologies may be limited in India, and its labour market and land use implications few, it could prove to be a highly efficient low-cost urban transport alternative compared to the hugely expensive metro systems of today.
- Tata Nano Autonomous: India’s First Driverless Car Is Under Process: As per a report that appeared in Times of India, John(practice head, robotics and cognitive systems at TCS) purchased a Nano to test the software in 2011. Daimler, Nissan, General Motors, BMW, Google and Tesla are investing big bucks in developing driverless cars across the world. John along with his 29-member team worked on the software and algorithms in their free time and created a 3D model to test it. Creating an algorithm using a custom cluster (multiple computers), the team were able to read all parameters of the engine. The car is also equipped with wheel encoders to measure the speed of the wheel, multiple lidars to identify obstacles around the car, HDR cameras and GPS. The data was processed by the software to make the car ‘drive’ like a human. Apart from this, pedal robots have been attached with the accelerator, brake, and clutch and connected them to the software. And once John will receive permission from the traffic police, this autonomous Tata Nano car will be tested on road.

figure 5.4 Tata Nano Autonomous
Drones
6.1 Problems and Solution
- Problem
- There are many industries where a lot of time and money was spent to survey remote areas plus it was not possible or very risky for humans to monitor or examine things in dangerous working conditions.
- For example monitoring locations for gas emissions, oil spills and damage, inspecting large boilers at power plants, monitoring the health of panels on solar farms, monitoring crops for diseases acros very wide spread fields.
- Solution
- Drones have come to rescue and proved very helpful in surveillance of all sites where it was very difficult / dangerous / time consuming / costly for humans to reach.
6.2 Basics of Drone
Drones have a long history as killer machines providing intelligence, surveillance, and reconnaissance for war managers. But over the years, their appeal has continued to extend beyond the corridors of military power. Commercially useful drones are not just remote-controlled aircraft, but, equipped with avionics, connections to ground control stations, sophisticated internal sensors that measure everything from yaw to acceleration, and GPS location capability. They are unmanned aircraft systems with increasing autonomy, whether fixed wing or rotary. With the advancement in drone technology, many companies have started putting sensors in their drones for collection of data. This data they collect can be used for various purposes.
There are different types of sensors that can be used in a drone to record different types of changes and collect a variety of information. Due to this, drones’ potential applicability pertaining to IoT has increased dramatically in the last few years, spanning multiple sectors, including Agriculture, Mining, Law Enforcement, manufacturing, Oil & Gas, Utilities, Media and Entertainment, and Infrastructure. A report released in 2015 by Business Insider projected a 19% annualized growth in market size for commercial and civilian drones between 2015 and 2020, as opposed to a 5% growth on the military front.

figure 6.1 Drone
Here are several use cases for drones by industry.
- Agriculture: Agriculture companies are now harnessing UAVs to monitor crops for diseases, assess yields, and identify the need for fertilizers in distinct environments. Farmers, on their part, have begun using drones to gain greater visibility into their assets, for revenue maximization.
- Telecom: Some wireless carriers are considering using drones built for cell tower maintenance. These drones help inspection teams gain a 360-degree overview of towers, without any manual involvement, thus eliminating the risk of fatalities and enabling easier detection of problems such as damaged cabling or equipment defects.
- Energy: Energy management is becoming more and more critical as developing countries advance their infrastructures. Drones can do dangerous jobs otherwise performed by humans, allowing for expedited maintenance on infrastructure. Drones also are inspecting large boilers at power plants, monitoring the health of panels on solar farms and assessing damage after storms.
- Oil and gas: Another industry that presents potential dangers for its workers, oil and gas, can benefit from using drones by monitoring locations for gas emissions, oil spills and damage that would otherwise be difficult and dangerous to reach, such as flare stacks, oil pipelines and offshore oil platforms.
- Construction: Construction sites present IoT with a number of fixable problems, including dangerous working conditions and lost items or machinery. That’s why several construction entities today rely on drones for site management, in terms of capturing, viewing and analyzing aerial imagery, monitoring job sites, inspecting structures and survey data.
No wonder businesses across different industries are increasingly adopting drones for a slew of commercial purposes, including for simplifying and automating complex workflows that entail increased operating costs and manual effort.
Conclusion
The Internet of Things promises to deliver a step change in individuals’ quality of life and enterprises’ productivity. Through a widely distributed, locally intelligent network of smart devices, the IoT has the potential to enable extensions and enhancements to fundamental services in transportation, logistics, security, utilities, education, healthcare and other areas, while providing a new ecosystem for application development.
A concerted effort is required to move the industry beyond the early stages of market development towards maturity, driven by common understanding of the distinct nature of the opportunity. This market has distinct characteristics in the areas of service distribution, business and charging models, capabilities required to deliver IoT services, and the differing demands these services will place on internet network.



